Macro Unit 14-15 主线
Published:
[Unit 14 & 15] Money Market
(PPT 15.1)
- Money Suppliers: HH, foreign entities
- Money Demanders: Firms, Gov’t
Money Market 的图中,纵轴是 Nominal Interest Rate,横轴是 QTY of Money。
- Money Supply 是一个固定的量,因此是一条竖直的线。
- 后文的 Monetary Policy 可以 shift 它。
- Money Demand 是一条斜向下的线。
- 这是因为:Opportunity Cost of holding money is the interest you could be earning from other financial assets. Interest Rate 越高,利息就越大,OC 就越大,人们就更愿意把钱存进银行。
- Shifters:
- Price Level
- PL 上升,MD 上升。
- Income
- Tech
- US Gov’t Borrowing
- Price Level
\[MS \uparrow \implies \text{Int Rate} \downarrow \implies \text{Investment} \uparrow \implies AD \uparrow\]
[Unit 15] Loanable Funds Market
(PPT 15.1)
It shows the supply and demand of loans & the equilibrium real interest rate.
(书 P289)Loanable Funds Market 的图中,纵轴是 Real Interest Rate,横轴是 QTY of Money(也可以写 QTY of Loanable Funds,这是书上的写法)。
- The supply of loanable funds is the amount of money that is saved. (from savers / lenders)
Private Saving: the amount that households save instead of consume.
Public Saving: the amount that the government saves instead of spends.
National Savings = public + private saving- Shifters
- Changes in private savings behavior
- Changes in public savings
- Changes in foreign investment (capital inflow & outflow)
- Demand:Borrowing is the demand of loanable funds. (from borrowers / investors)
- Shifters
- Changes in borrowing by consumers
- Changes in borrowing by businesses (investment spending)
- Changes in borrowing by the government
- Gov’t Deficit Spending: Spending > Tax
- Shifters
(再次吟唱:Opportunity Cost of holding money is the interest you could be earning from other financial assets.)利率越高,OC 越高,人们就更想把钱放在银行里,而更不愿意从银行拿钱。因此 S 斜向上,D 斜向下。
e.g. 当 political instability 发生:
- demand 左移,因为 investment 下降
- supply 左移,因为外国投资者会把资本收回去,资本外逃(capital flight)。
Example (2023 MCQ #4)
Assume that the country of Alpha has a balanced budget. If the government and central bank of Alpha implement expansionary fiscal and monetary policies in order to address a recession, what effect would these policies have in the short run on the government budget and interest rates?
首先 Government Budget Deficit 不用说。
TODO:
[Unit 14] Fractional Reserve Banking
Fractional Reserve System 也叫 Limited Reserve System。
Fractional Reserve Banking
(PPT 14.1)
- Demand Deposit: Money deposited in a commercial bank in a checking account.
- Required Reserve: The percent that banks must hold by law.
- Excess Reserve: The amount that the bank can loan out or invest.
银行拿到一笔 Demand Deposit 时,会将其分为 3 个部分:
- Required Reserve:法律规定的,动不了。
- Excess Reserve:银行自己决定要拿手里的。(当然也可能不拿)
- Loanable Fund:借出去!
Money Expansion Process
借出去的部分会进入其它银行并重复这一过程。
Assume that banks keep no excess reserves, and there are no cash leakages. 每一笔钱出去之后就会进入其它银行。
模拟一下这个过程:
- 银行 A 拿到了一笔 Demand Deposit $a$ 刀。
- 银行 A 留住 $RR \times a$ 刀,借出 $(1 - RR) a$ 刀,进入银行 B。
- 创造了 $(1 - RR) a$ 刀的 money supply。
- 注:怎么创造的呢?原始存款人的账户上有 $a$ 刀,借款人获得贷款之后,账户上会有 $(1 - RR) a$ 刀,总 MS 就比原先多出来了这一部分。
- 创造了 $(1 - RR) a$ 刀的 money supply。
- 银行 B 留住 $RR (1 - RR) a$ 刀,借出 $(1-RR)^2 a$ 刀,进入银行 C。
- 创造了 $(1-RR)^2 a$ 刀的 MS。
以此类推,对于一笔凭空冒出的 Demand Deposit,总 $\Delta MS$ 的计算公式为:
\[\Delta MS = a \sum\limits_{n=0}^\infty (1 - RR)^n = \frac a {RR}\]即原先的一笔钱被放大了 $\frac 1 {RR}$ 倍:
\[\boxed{\text{Money Multiplier} = \frac 1 {\text{Reserve Requirement}}}\] \[\boxed{\Delta MS = \text{Money Multiplier} \times \text{Change in Bank Reserves}}\]Money Multiplier 也叫 Simple Multiplier。(2012 MCQ #38)
⭐[Unit 14] Ample Reserve
巴朗书上没有这一段啊
(Katie 上课)
- Commercial Banks 问美联储借钱,美联储收利息的利率叫 Discount Rate。
- Commercial Banks 在美联储存钱,收到利息的利率叫 Interest on Reserve,也叫 Administered Policy Rate。
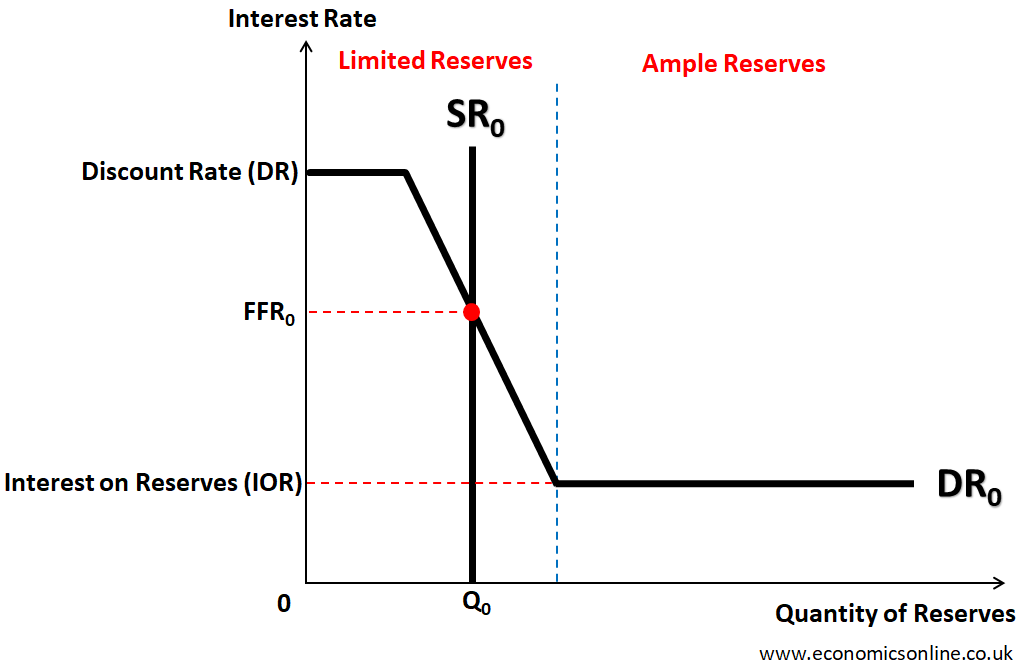
Graph: Reserve MKT
Katie 上课画的版本是:纵轴是 Policy Rate,横轴是 Quantity of Money。(也可以写 Quantity of Reserves)
Policy Rate (也叫 Federal Funds Rate),是商业银行之间互相借钱的利息。
- 正常情况下(当 Commercial Banks 的 Reserve 量适中,Limited Reserve),Demand 是斜向下曲线。
- 银行之间的供需关系决定 Interest Rate。准备金供给增加时,银行间借贷竞争减弱,利率下降。准备金减少时,银行更愿意支付高利率借款,利率上升。(Deepseek)
- 当利率高到一定程度时(Reserve 特别小),找其他银行借还不如找美联储,此时 Interest Rate 被 Discount Rate 完全拦住。
- 当利率高到一定程度时(Reserve 特别大,也就是 Ample Reserve),把钱放给别人还不如存在美联储拿的利息多,此时 Interest Rate 被 Interest on Reserve 完全拦住。
从 Google 上找的一个图:来源
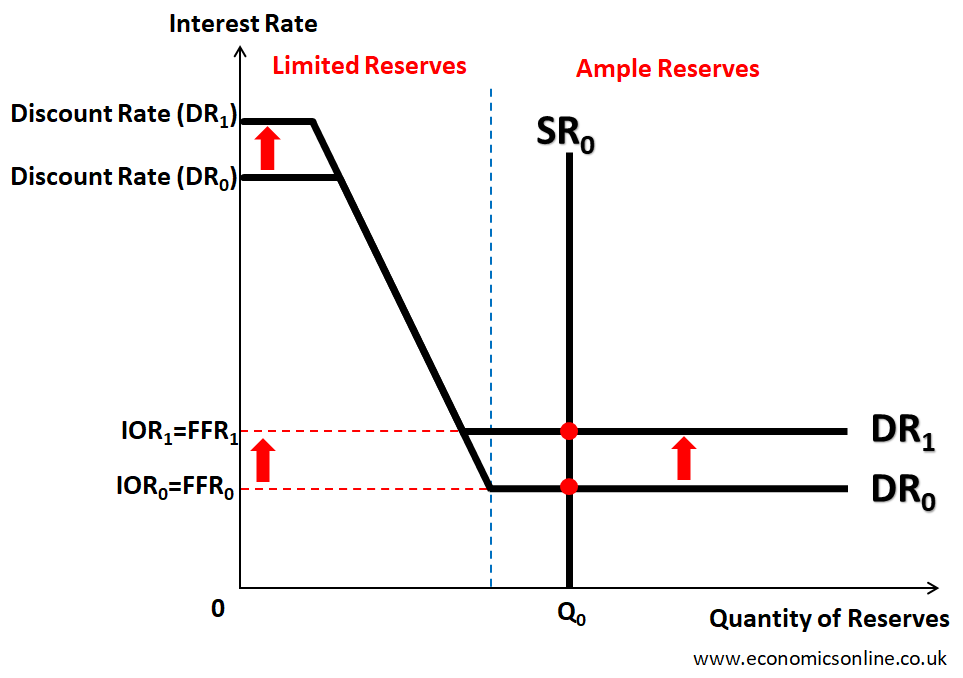
Discount Rate 和 Interest on Reserve 是联动的,要同时上调或下降:
[Unit 14] Monetary Policy
现在出现了 Recession,你作为美联储,你要实施 Expansionary Monetary Policy(也叫 Easy Monetary Policy,增大 $MS$,以刺激经济。(反之,冷却经济的政策叫做 Contractionary Monetary Policy,也叫 Tight Monetary Policy)
美联储有四板斧:
\[\text{Expansionary} \begin{cases} \text{Limited Reserve} & \begin{cases} \text{Discount Rate} \downarrow \\ \text{Required Reserve} \downarrow \\ \text{Buy Bonds at Secondary MKT} \end{cases} \\ \text{Ample Reserve} & \begin{cases} \text{Interest on Reserve} \downarrow \\ \end{cases} \\ \end{cases}\]- Limited Reserve
- Decrease Discount Rate: 降低银行向 Fed 借钱的成本,让银行更愿意借钱,借到钱之后通过 Money Multiplier 翻倍。
- Decrease Required Reserve: 让 Money Multiplier 增加。
- Buy Bonds at Secondary Market (Open Market Operations): 买已有的 bonds,把自己的钱送出去。
- Secondary Market: the place to trade securities which have been issued at the primary MKT.
- Ample Reserve 中不用这个的原因是,给银行送钱之后,银行会存回 Fed 拿 interest on reserve 的利息。
- Ample Reserve
- Decrease Interest on Reserve: 降低银行在 Fed 这里获得的收益,让银行更愿意把钱拿去放贷。